
It has a total of 7 nucleons (neutrons and protons) so therefore 7 x the mass of the neutron/proton. 7 3Li Nucleus = The nucleus has 3 protons and 4 neutrons, neutrons have a charge of 0 so the charge of the nucleus is 3 x the charge of the proton.The electron has the highest specific charge the neutron has the lowest. In short, if an atom loses an electron it will lose 1e (1.6×10 -19), and if it gains an electron, it will gain 1e. Therefore, the specific charge of the newly formed ion would be -2e divided by its mass. The charge on an atom will always be 0, so if an atom loses two electrons, that is 2 x (1.6 x 10 -19) of charge lost, or -2e. The equation for it therefore, is: Specific Charge = Charge/Mass. Specific charge is the charge to mass ratio of an atom/ion or other mass. The nucleus sits in the middle of the atom with negatively charged electrons orbiting it. Meaning of isotopes and the use of isotopic data.įrom Rutherford’s experiment we understand that the atom consists of positively charged protons with neutral neutrons in one place, called a nucleus.Students should be familiar with the A Z X notation.
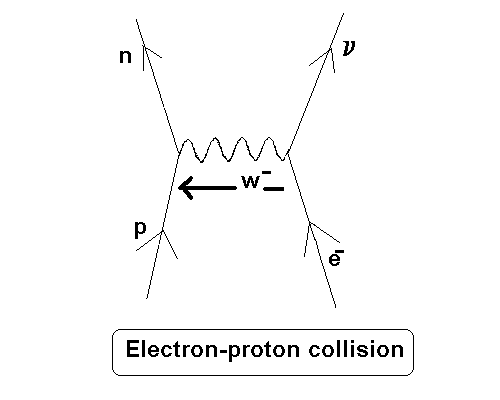

In addition, a wiggly line is used to represent the exchange particle.
Electron capture feynman diagram series#
Richard Feynman came up with a graphical representation of interactions, while taking into account the exchange particle or force carrier particle that plays the crucial role in them.įeynman diagrams use a series of lines and vertices to illustrate the particle interactions. There are four fundamental forces in nature. He made a great contribution in promoting particle physics as well, using his other famous skill, in addition to being a brilliant scientist - ability to teach and share his knowledge in such a way that an audience could effortlessly understands it - and enjoy it too in equal measure.įeynman's great contribution to the QED made him a recipient to share the Nobel prize for physics in 1965.The diagrams, which he came up with to explain the interaction between the sub atomic particles, came to be known as Feynman Diagrams, left an indelible mark in his illustrious legacy for years to come. Richard Feynman, born in 1918, was an American theoretical physicist, who played a major role in the field of quantum electrodynamics(QED) with a significant contribution.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
